ENS-DNS Redirection
How ETH.me Retrieves Data from ENS
ETH.me functions akin to a reverse proxy for the ENS and IPFS protocols, enabling access via HTTPS through client-side browsers.
When a user sends an HTTPS request to name.eth.me, our wildcard DNS record *.eth.me captures the request. The server then informs the client's browser of the corresponding ENS names. Subsequently, the browser's web3.js accesses the default ENS resolver contract on the Ethereum mainnet. The frontend JavaScript then redirects the browser to the appropriate URL, following the redirection rules outlined in the "Redirection Rules" section. The interaction between user-end browser, ETH.me and Ethereum blockchain can be described by the picture below:
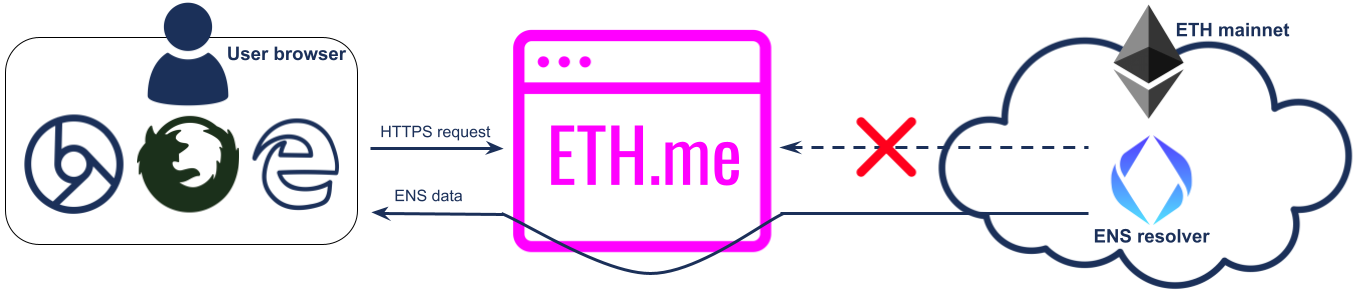
Redirection Rules
ETH.me can redirect a DNS request such as name.eth.me to any link specified in the ENS domain records of name.eth. This includes links to platforms like Twitter, GitHub, LinkedIn, and IPFS.
To determine the redirection target, the ENS domain owner should set a subfield named index. When a user requests a URL at name.eth, ETH.me, by default, searches for the index record. The value of the index field indicates another field. For instance, if set to com.twitter, ETH.me will redirect to the URL specified in the com.twitter field. You should set 2 ENS records to setup the twitter link redirection:
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| index | com.twitter |
| com.twitter | TaxaNetwork |
If the index field value is unset, ETH.me will check content hash field value and redirect to it. If content hash is not set as well, it will check url field and redirect to it. If all three fields index, content hash and url are unset, then it will redirect to the ENS domain's detail page.
ENS Subfields Reference
The following table outlines the various subfields recognized by ETH.me for redirection purposes:
| Name | Comment |
|---|---|
| index | The primary field for redirection |
| content hash | URL of an IPFS resource |
| com.twitter | Twitter username |
| url | Any arbitrary HTTPS URL |
| com.github | GitHub username |
| com.opensea | OpenSea username |
| com.telegram | Telegram username |
| com.reddit | Reddit username |
| com.linkedin | Linkedin username |
| com.etherscan | Etherscan address |
Setting up IPFS URLs
Setting up a decentralized web3 website involves utilizing protocols like IPFS and ENS. Firstly we will need a static website or webpage to upload it to IPFS. There are several methods to upload files to IPFS, some of which are listed below.
Using Pinning Service
An easy way to upload & pin your files to IPFS is to use a pinning service. The benefit of using pinning services is they run lots of IPFS nodes so you don't have to run your own IPFS node to make sure that your website is accessible..
- Go to Pinata.cloud and sign up or log in.
- Once you are logged in, on Dashboard select
Uploadand clickBrowse. - Navigate to your website folder and click
Open. - After that, click
Upload. - Once uploaded you can see your folder/file pinned & listed on dashboard. You can copy the CID from your listed file and use it in IPFS format, like this
ipfs://CID,ipfs://QmUFrzU2YfTgwhQaQ2RAZ2Pi2fAd75KwWSz6tYJT7yMFqv
Using Fleek
Fleek is a service similar to Netlify, but for Web3 applications. Once you've pushed your changes to git, Fleek builds, pins, and updates your site on IPFS.
- Upload your website to Github.
- Go to Fleek and sign in using your Github account.
- Once logged in, click
Add new siteand selectIPFSas Hosting service. - Click
Deploy site. - Once the site is deployed, copy the CID from
Deploy Logand prependipfs://.
More details on Fleek deployment can be found here, in IPFS docs.
Deploying your Own Node
If you want to run your own IPFS node you can,
- Download & install the IPFS desktop from IPFS desktop downloads page.
- Open IPFS desktop and go to the Files page.
- Click
add fileand select your webpage. - Once added click the three dot menu on your file, and copy
CID. - In order to keep the content long term you need to pin the files. Click three dot menu on your file, and click
Pin.
More details on hosting file on your own node can be found here, in IPFS docs.
Link ENS and IPFS
Once you have uploaded your website on IPFS, you can link it to your ENS Name by setting the contenthash record. This can be done using the ENS Manager.
- Go to ENS Manager App.
- Select your ENS name you want to link your IPFS to.
- Navigate to the
Recordstab and clickEdit Records. - Then go to
Othertab, and in the Content hash field enter your IPFS link (like this,ipfs://QmUFrzU2YfTgwhQaQ2RAZ2Pi2fAd75KwWSz6tYJT7yMFqv). - Click save and confirm transaction.
A detailed step by step guide on IPFS Uploading and Linking IPFS with ENS Name can be found here, in ENS Domains article.